Electronic
Code of Federal Regulations
e-CFR
data is current as of July 23, 2019
|
|
|
Subpart
D—Walking-Working Surfaces
Authority:
29 U.S.C. 653, 655, and 657; Secretary of Labor's Order No. 12-71
(36 FR 8754), 8-76 (41 FR 25059), 9-83 (48 FR 35736), 1-90 (55 FR
9033), and 1-2012 (77 FR 3912), as applicable; and 29 CFR part
1911.
Source:
81 FR 82981, Nov. 18, 2016, unless otherwise noted.
§1910.21 Scope
and definitions.
(a)
Scope.
This subpart applies to all general industry workplaces. It covers
all walking-working surfaces unless specifically excluded by an
individual section of this subpart.
(b)
Definitions.
The following definitions apply in this subpart:
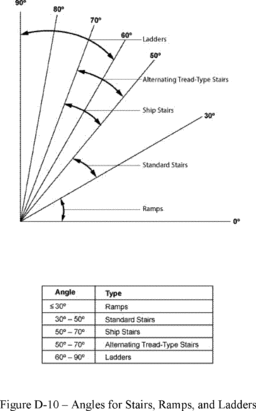
Alternating
tread-type stair
means a type of stairway consisting of a series of treads that
usually are attached to a center support in an alternating manner
such that an employee typically does not have both feet on the
same level while using the stairway.
Anchorage
means a secure point of attachment for equipment such as
lifelines, lanyards, deceleration devices, and rope descent
systems.
Authorized
means an employee who the employer assigns to perform a specific
type of duty, or allows in a specific location or area.
Cage
means an enclosure mounted on the side rails of a fixed ladder or
fastened to a structure behind the fixed ladder that is designed
to surround the climbing space of the ladder. A cage also is
called a “cage guard” or “basket guard.”
Carrier
means the track of a ladder safety system that consists of a
flexible cable or rigid rail attached to the fixed ladder or
immediately adjacent to it.
Combination
ladder
means a portable ladder that can be used as a stepladder,
extension ladder, trestle ladder, or stairway ladder. The
components of a combination ladder also may be used separately as
a single ladder.
Dangerous
equipment
means equipment, such as vats, tanks, electrical equipment,
machinery, equipment or machinery with protruding parts, or other
similar units, that, because of their function or form, may harm
an employee who falls into or onto the equipment.
Designated
area
means a distinct portion of a walking-working surface delineated
by a warning line in which employees may perform work without
additional fall protection.
Dockboard
means a portable or fixed device that spans a gap or compensates
for a difference in elevation between a loading platform and a
transport vehicle. Dockboards include, but are not limited to,
bridge plates, dock plates, and dock levelers.
Equivalent
means alternative designs, equipment, materials, or methods, that
the employer can demonstrate will provide an equal or greater
degree of safety for employees compared to the designs, equipment,
materials, or methods specified in this subpart.
Extension
ladder
means a non-self-supporting portable ladder that is adjustable in
length.
Failure
means a load refusal, breakage, or separation of component parts.
A load refusal is the point at which the ultimate strength of a
component or object is exceeded.
Fall
hazard
means any condition on a walking-working surface that exposes an
employee to a risk of harm from a fall on the same level or to a
lower level.
Fall
protection
means any equipment, device, or system that prevents an employee
from falling from an elevation or mitigates the effect of such a
fall.
Fixed
ladder
means a ladder with rails or individual rungs that is permanently
attached to a structure, building, or equipment. Fixed ladders
include individual-rung ladders, but not ship stairs, step bolts,
or manhole steps.
Grab
bar
means an individual horizontal or vertical handhold installed to
provide access above the height of the ladder.
Guardrail
system
means a barrier erected along an unprotected or exposed side,
edge, or other area of a walking-working surface to prevent
employees from falling to a lower level.
Handrail
means a rail used to provide employees with a handhold for
support.
Hoist
area
means any elevated access opening to a walking-working surface
through which equipment or materials are loaded or received.
Hole
means a gap or open space in a floor, roof, horizontal
walking-working surface, or similar surface that is at least 2
inches (5 cm) in its least dimension.
Individual-rung
ladder
means a ladder that has rungs individually attached to a building
or structure. An individual-rung ladder does not include manhole
steps.
Ladder
means a device with rungs, steps, or cleats used to gain access to
a different elevation.
Ladder
safety system
means a system designed to eliminate or reduce the possibility of
falling from a ladder. A ladder safety system usually consists of
a carrier, safety sleeve, lanyard, connectors, and body harness.
Cages and wells are not ladder safety systems.
Low-slope
roof
means a roof that has a slope less than or equal to a ratio of 4
in 12 (vertical to horizontal).
Lower
level
means a surface or area to which an employee could fall. Such
surfaces or areas include, but are not limited to, ground levels,
floors, roofs, ramps, runways, excavations, pits, tanks,
materials, water, equipment, and similar surfaces and structures,
or portions thereof.
Manhole
steps
means steps that are individually attached to, or set into, the
wall of a manhole structure.
Maximum
intended load
means the total load (weight and force) of all employees,
equipment, vehicles, tools, materials, and other loads the
employer reasonably anticipates to be applied to a walking-working
surface at any one time.
Mobile
means manually propelled or moveable.
Mobile
ladder stand
(ladder stand) means a mobile, fixed-height, self-supporting
ladder that usually consists of wheels or casters on a rigid base
and steps leading to a top step. A mobile ladder stand also may
have handrails and is designed for use by one employee at a time.
Mobile
ladder stand platform
means a mobile, fixed-height, self-supporting unit having one or
more standing platforms that are provided with means of access or
egress.
Open
riser
means the gap or space between treads of stairways that do not
have upright or inclined members (risers).
Opening
means a gap or open space in a wall, partition, vertical
walking-working surface, or similar surface that is at least 30
inches (76 cm) high and at least 18 inches (46 cm) wide, through
which an employee can fall to a lower level.
Personal
fall arrest system
means a system used to arrest an employee in a fall from a
walking-working surface. It consists of a body harness, anchorage,
and connector. The means of connection may include a lanyard,
deceleration device, lifeline, or a suitable combination of these.
Personal
fall protection system
means a system (including all components) an employer uses to
provide protection from falling or to safely arrest an employee's
fall if one occurs. Examples of personal fall protection systems
include personal fall arrest systems, positioning systems, and
travel restraint systems.
Platform
means a walking-working surface that is elevated above the
surrounding area.
Portable
ladder
means a ladder that can readily be moved or carried, and usually
consists of side rails joined at intervals by steps, rungs, or
cleats.
Positioning
system
(work-positioning system) means a system of equipment and
connectors that, when used with a body harness or body belt,
allows an employee to be supported on an elevated vertical
surface, such as a wall or window sill, and work with both hands
free. Positioning systems also are called “positioning
system devices” and “work-positioning equipment.”
Qualified
describes a person who, by possession of a recognized degree,
certificate, or professional standing, or who by extensive
knowledge, training, and experience has successfully demonstrated
the ability to solve or resolve problems relating to the subject
matter, the work, or the project.
Ramp
means an inclined walking-working surface used to access another
level.
Riser
means the upright (vertical) or inclined member of a stair that is
located at the back of a stair tread or platform and connects
close to the front edge of the next higher tread, platform, or
landing.
Rope
descent system
means a suspension system that allows an employee to descend in a
controlled manner and, as needed, stop at any point during the
descent. A rope descent system usually consists of a roof
anchorage, support rope, a descent device, carabiner(s) or
shackle(s), and a chair (seatboard). A rope descent system also is
called controlled descent equipment or apparatus. Rope descent
systems do not include industrial rope access systems.
Rung,
step, or cleat
means the cross-piece of a ladder on which an employee steps to
climb up and down.
Runway
means an elevated walking-working surface, such as a catwalk, a
foot walk along shafting, or an elevated walkway between
buildings.
Scaffold
means any temporary elevated or suspended platform and its
supporting structure, including anchorage points, used to support
employees, equipment, materials, and other items. For purposes of
this subpart, a scaffold does not include a crane-suspended or
derrick-suspended personnel platform or a rope descent system.
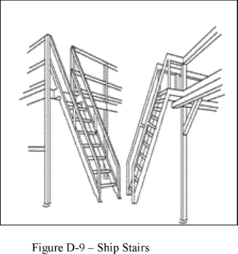
Ship
stair
(ship ladder) means a stairway that is equipped with treads, stair
rails, and open risers, and has a slope that is between 50 and 70
degrees from the horizontal.
Side-step
ladder
means a type of fixed ladder that requires an employee to step
sideways from it in order to reach a walking-working surface, such
as a landing.
Spiral
stairs
means a series of treads attached to a vertical pole in a winding
fashion, usually within a cylindrical space.
Stair
rail or stair rail system
means a barrier erected along the exposed or open side of
stairways to prevent employees from falling to a lower level.
Stairway
(stairs)
means risers and treads that connect one level with another, and
includes any landings and platforms in between those levels.
Stairways include standard, spiral, alternating tread-type, and
ship stairs.
Standard
stairs
means a fixed or permanently installed stairway. Ship, spiral, and
alternating tread-type stairs are not considered standard stairs.
Step
bolt
(pole step) means a bolt or rung attached at intervals along a
structural member used for foot placement and as a handhold when
climbing or standing.
Stepladder
means a self-supporting, portable ladder that has a fixed height,
flat steps, and a hinged back.
Stepstool
means a self-supporting, portable ladder that has flat steps and
side rails. For purposes of the final rule, stepstool includes
only those ladders that have a fixed height, do not have a pail
shelf, and do not exceed 32 inches (81 cm) in overall height to
the top cap, although side rails may extend above the top cap. A
stepstool is designed so an employee can climb and stand on all of
the steps and the top cap.
Through
ladder
means a type of fixed ladder that allows the employee to step
through the side rails at the top of the ladder to reach a
walking-working surface, such as a landing.
Tieback
means an attachment between an anchorage (e.g.,
structural member) and a supporting device (e.g.,
parapet clamp or cornice hook).
Toeboard
means a low protective barrier that is designed to prevent
materials, tools, and equipment from falling to a lower level, and
protect employees from falling.
Travel
restraint system
means a combination of an anchorage, anchorage connector, lanyard
(or other means of connection), and body support that an employer
uses to eliminate the possibility of an employee going over the
edge of a walking-working surface.
Tread
means a horizontal member of a stair or stairway, but does not
include landings or platforms.
Unprotected
sides and edges
mean any side or edge of a walking-working surface (except at
entrances and other points of access) where there is no wall,
guardrail system, or stair rail system to protect an employee from
falling to a lower level.
Walking-working
surface
means any horizontal or vertical surface on or through which an
employee walks, works, or gains access to a work area or workplace
location.
Warning
line
means a barrier erected to warn employees that they are
approaching an unprotected side or edge, and which designates an
area in which work may take place without the use of other means
of fall protection.
Well
means a permanent, complete enclosure around a fixed ladder.
§1910.22 General
requirements.
(a)
Surface
conditions.
The employer must ensure:
(1)
All places of employment, passageways, storerooms, service rooms,
and walking-working surfaces are kept in a clean, orderly, and
sanitary condition.
(2)
The floor of each workroom is maintained in a clean and, to the
extent feasible, in a dry condition. When wet processes are used,
drainage must be maintained and, to the extent feasible, dry
standing places, such as false floors, platforms, and mats must be
provided.
(3)
Walking-working surfaces are maintained free of hazards such as
sharp or protruding objects, loose boards, corrosion, leaks,
spills, snow, and ice.
(b)
Loads.
The employer must ensure that each walking-working surface can
support the maximum intended load for that surface.
(c)
Access
and egress.
The employer must provide, and ensure each employee uses, a safe
means of access and egress to and from walking-working surfaces.
(d)
Inspection,
maintenance, and repair.
The employer must ensure:
(1)
Walking-working surfaces are inspected, regularly and as
necessary, and maintained in a safe condition;
(2)
Hazardous conditions on walking-working surfaces are corrected or
repaired before an employee uses the walking-working surface
again. If the correction or repair cannot be made immediately, the
hazard must be guarded to prevent employees from using the
walking-working surface until the hazard is corrected or repaired;
and
(3)
When any correction or repair involves the structural integrity of
the walking-working surface, a qualified person performs or
supervises the correction or repair.
§1910.23 Ladders.
(a)
Application.
The employer must ensure that each ladder used meets the
requirements of this section. This section covers all ladders,
except when the ladder is:
(1)
Used in emergency operations such as firefighting, rescue, and
tactical law enforcement operations, or training for these
operations; or
(2)
Designed into or is an integral part of machines or equipment.
(b)
General
requirements for all ladders.
The employer must ensure:
(1)
Ladder rungs, steps, and cleats are parallel, level, and uniformly
spaced when the ladder is in position for use;
(2)
Ladder rungs, steps, and cleats are spaced not less than 10 inches
(25 cm) and not more than 14 inches (36 cm) apart, as measured
between the centerlines of the rungs, cleats, and steps, except
that:
(i)
Ladder rungs and steps in elevator shafts must be spaced not less
than 6 inches (15 cm) apart and not more than 16.5 inches (42 cm)
apart, as measured along the ladder side rails; and
(ii)
Fixed ladder rungs and steps on telecommunication towers must be
spaced not more than 18 inches (46 cm) apart, measured between the
centerlines of the rungs or steps;
(3)
Steps on stepstools are spaced not less than 8 inches (20 cm)
apart and not more than 12 inches (30 cm) apart, as measured
between the centerlines of the steps;
(4)
Ladder rungs, steps, and cleats have a minimum clear width of 11.5
inches (29 cm) on portable ladders and 16 inches (41 cm) (measured
before installation of ladder safety systems) for fixed ladders,
except that:
(i)
The minimum clear width does not apply to ladders with narrow
rungs that are not designed to be stepped on, such as those
located on the tapered end of orchard ladders and similar ladders;
(ii)
Rungs and steps of manhole entry ladders that are supported by the
manhole opening must have a minimum clear width of 9 inches (23
cm);
(iii)
Rungs and steps on rolling ladders used in telecommunication
centers must have a minimum clear width of 8 inches (20 cm); and
(iv)
Stepstools have a minimum clear width of 10.5 inches (26.7 cm);
(5)
Wooden ladders are not coated with any material that may obscure
structural defects;
(6)
Metal ladders are made with corrosion-resistant material or
protected against corrosion;
(7)
Ladder surfaces are free of puncture and laceration hazards;
(8)
Ladders are used only for the purposes for which they were
designed;
(9)
Ladders are inspected before initial use in each work shift, and
more frequently as necessary, to identify any visible defects that
could cause employee injury;
(10)
Any ladder with structural or other defects is immediately tagged
“Dangerous: Do Not Use” or with similar language in
accordance with §1910.145 and removed from service until
repaired in accordance with §1910.22(d), or replaced;
(11)
Each employee faces the ladder when climbing up or down it;
(12)
Each employee uses at least one hand to grasp the ladder when
climbing up and down it; and
(13)
No employee carries any object or load that could cause the
employee to lose balance and fall while climbing up or down the
ladder.
(c)
Portable
ladders.
The employer must ensure:
(1)
Rungs and steps of portable metal ladders are corrugated, knurled,
dimpled, coated with skid-resistant material, or otherwise treated
to minimize the possibility of slipping;
(2)
Each stepladder or combination ladder used in a stepladder mode is
equipped with a metal spreader or locking device that securely
holds the front and back sections in an open position while the
ladder is in use;
(3)
Ladders are not loaded beyond the maximum intended load;
Note
to paragraph (c)(3):
The maximum intended load, as defined in §1910.21(b),
includes the total load (weight and force) of the employee and all
tools, equipment, and materials being carried.
(4)
Ladders are used only on stable and level surfaces unless they are
secured or stabilized to prevent accidental displacement;
(5)
No portable single rail ladders are used;
(6)
No ladder is moved, shifted, or extended while an employee is on
it;
(7)
Ladders placed in locations such as passageways, doorways, or
driveways where they can be displaced by other activities or
traffic:
(i)
Are secured to prevent accidental displacement; or
(ii)
Are guarded by a temporary barricade, such as a row of traffic
cones or caution tape, to keep the activities or traffic away from
the ladder;
(8)
The cap (if equipped) and top step of a stepladder are not used as
steps;
(9)
Portable ladders used on slippery surfaces are secured and
stabilized;
(10)
The top of a non-self-supporting ladder is placed so that both
side rails are supported, unless the ladder is equipped with a
single support attachment;
(11)
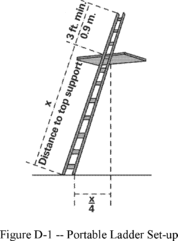
Portable ladders used to gain access to an upper landing surface
have side rails that extend at least 3 feet (0.9 m) above the
upper landing surface (see Figure D-1 of this section);
(12)
Ladders and ladder sections are not tied or fastened together to
provide added length unless they are specifically designed for
such use;
(13)
Ladders are not placed on boxes, barrels, or other unstable bases
to obtain additional height.
View
or download PDF
(d)
Fixed
ladders.
The employer must ensure:
(1)
Fixed ladders are capable of supporting their maximum intended
load;
(2)
The minimum perpendicular distance from the centerline of the
steps or rungs, or grab bars, or both, to the nearest permanent
object in back of the ladder is 7 inches (18 cm), except for
elevator pit ladders, which have a minimum perpendicular distance
of 4.5 inches (11 cm);
(3)
Grab bars do not protrude on the climbing side beyond the rungs of
the ladder that they serve;
(4)
The side rails of through or side-step ladders extend 42 inches
(1.1 m) above the top of the access level or landing platform
served by the ladder. For parapet ladders, the access level is:
(i)
The roof, if the parapet is cut to permit passage through the
parapet; or
(ii)
The top of the parapet, if the parapet is continuous;
(5)
For through ladders, the steps or rungs are omitted from the
extensions, and the side rails are flared to provide not less than
24 inches (61cm) and not more than 30 inches (76 cm) of clearance.
When a ladder safety system is provided, the maximum clearance
between side rails of the extension must not exceed 36 inches (91
cm);
(6)
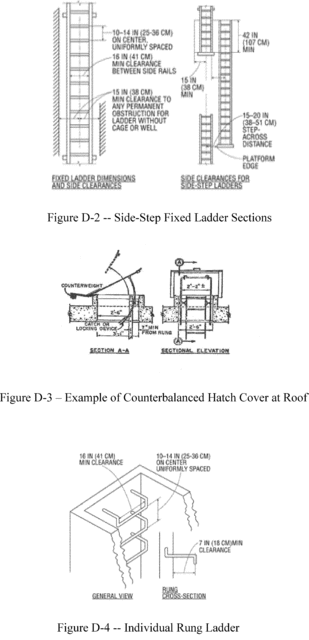
For side-step ladders, the side rails, rungs, and steps must be
continuous in the extension (see Figure D-2 of this section);
(7)
Grab bars extend 42 inches (1.1 m) above the access level or
landing platforms served by the ladder;
(8)
The minimum size (cross-section) of grab bars is the same size as
the rungs of the ladder.
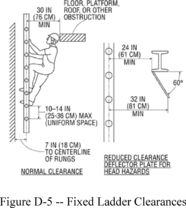
(9)
When a fixed ladder terminates at a hatch (see Figure D-3 of this
section), the hatch cover:
(i)
Opens with sufficient clearance to provide easy access to or from
the ladder; and
(ii)
Opens at least 70 degrees from horizontal if the hatch is
counterbalanced;
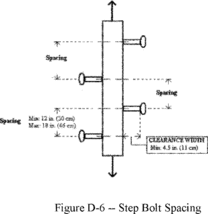
(10)
Individual-rung ladders are constructed to prevent the employee's
feet from sliding off the ends of the rungs (see Figure D-4 of
this section);
(11)
Fixed ladders having a pitch greater than 90 degrees from the
horizontal are not used;
(12)
The step-across distance from the centerline of the rungs or steps
is:
(i)
For through ladders, not less than 7 inches (18 cm) and not more
than 12 inches (30 cm) to the nearest edge of the structure,
building, or equipment accessed from the ladders;
(ii)
For side-step ladders, not less than 15 inches (38 cm) and not
more than 20 inches (51 cm) to the access points of the platform
edge;
(13)
Fixed ladders that do not have cages or wells have:
(i)
A clear width of at least 15 inches (38 cm) on each side of the
ladder centerline to the nearest permanent object; and
(ii)
A minimum perpendicular distance of 30 inches (76 cm) from the
centerline of the steps or rungs to the nearest object on the
climbing side. When unavoidable obstructions are encountered, the
minimum clearance at the obstruction may be reduced to 24 inches
(61 cm), provided deflector plates are installed (see Figure D-5
of this section).
Note
to paragraph (d):
Section 1910.28 establishes the employer's duty to provide fall
protection for employees on fixed ladders, and §1910.29
specifies the criteria for fall protection systems for fixed
ladders.
View
or download PDF
View
or download PDF
(e)
Mobile
ladder stands and mobile ladder stand platforms—(1)
General
requirements.
The employer must ensure:
(i)
Mobile ladder stands and platforms have a step width of at least
16 inches (41 cm);
(ii)
The steps and platforms of mobile ladder stands and platforms are
slip resistant. Slip-resistant surfaces must be either an integral
part of the design and construction of the mobile ladder stand and
platform, or provided as a secondary process or operation, such as
dimpling, knurling, shotblasting, coating, spraying, or applying
durable slip-resistant tapes;
(iii)
Mobile ladder stands and platforms are capable of supporting at
least four times their maximum intended load;
(iv)
Wheels or casters under load are capable of supporting their
proportional share of four times the maximum intended load, plus
their proportional share of the unit's weight;
(v)
Unless otherwise specified in this section, mobile ladder stands
and platforms with a top step height of 4 feet (1.2 m) or above
have handrails with a vertical height of 29.5 inches (75 cm) to 37
inches (94 cm), measured from the front edge of a step. Removable
gates or non-rigid members, such as chains, may be used instead of
handrails in special-use applications;
(vi)
The maximum work-surface height of mobile ladder stands and
platforms does not exceed four times the shortest base dimension,
without additional support. For greater heights, outriggers,
counterweights, or comparable means that stabilize the mobile
ladder stands and platforms and prevent overturning must be used;
(vii)
Mobile ladder stands and platforms that have wheels or casters are
equipped with a system to impede horizontal movement when an
employee is on the stand or platform; and
(viii)
No mobile ladder stand or platform moves when an employee is on
it.
(2)
Design
requirements for mobile ladder stands.
The employer must ensure:
(i)
Steps are uniformly spaced and arranged, with a rise of not more
than 10 inches (25 cm) and a depth of not less than 7 inches (18
cm). The slope of the step stringer to which the steps are
attached must not be more than 60 degrees, measured from the
horizontal;
(ii)
Mobile ladder stands with a top step height above 10 feet (3 m)
have the top step protected on three sides by a handrail with a
vertical height of at least 36 inches (91 cm); and top steps that
are 20 inches (51 cm) or more, front to back, have a midrail and
toeboard. Removable gates or non-rigid members, such as chains,
may be used instead of handrails in special-use applications; and
(iii)
The standing area of mobile ladder stands is within the base
frame.
(3)
Design
requirements for mobile ladder stand platforms.
The employer must ensure:
(i)
Steps of mobile ladder stand platforms meet the requirements of
paragraph (e)(2)(i) of this section. When the employer
demonstrates that the requirement is not feasible, steeper slopes
or vertical rung ladders may be used, provided the units are
stabilized to prevent overturning;
(ii)
Mobile ladder stand platforms with a platform height of 4 to 10
feet (1.2 m to 3 m) have, in the platform area, handrails with a
vertical height of at least 36 inches (91 cm) and midrails; and
(iii)
All ladder stand platforms with a platform height above 10 feet (3
m) have guardrails and toeboards on the exposed sides and ends of
the platform.
(iv)
Removable gates or non-rigid members, such as chains, may be used
on mobile ladder stand platforms instead of handrails and
guardrails in special-use applications.
§1910.24 Step
bolts and manhole steps.
(a)
Step
bolts.
The employer must ensure:
(1)
Each step bolt installed on or after January 17, 2017 in an
environment where corrosion may occur is constructed of, or coated
with, material that protects against corrosion;
(2)
Each step bolt is designed, constructed, and maintained to prevent
the employee's foot from slipping off the end of the step bolt;
(3)
Step bolts are uniformly spaced at a vertical distance of not less
than 12 inches (30 cm) and not more than 18 inches (46 cm) apart,
measured center to center (see Figure D-6 of this section). The
spacing from the entry and exit surface to the first step bolt may
differ from the spacing between the other step bolts;
(4)
Each step bolt has a minimum clear width of 4.5 inches (11 cm);
(5)
The minimum perpendicular distance between the centerline of each
step bolt to the nearest permanent object in back of the step bolt
is 7 inches (18 cm). When the employer demonstrates that an
obstruction cannot be avoided, the distance must be at least 4.5
inches (11 cm);
(6)
Each step bolt installed before January 17, 2017 is capable of
supporting its maximum intended load;
(7)
Each step bolt installed on or after January 17, 2017 is capable
of supporting at least four times its maximum intended load;
(8)
Each step bolt is inspected at the start of the workshift and
maintained in accordance with §1910.22; and
(9)
Any step bolt that is bent more than 15 degrees from the
perpendicular in any direction is removed and replaced with a step
bolt that meets the requirements of this section before an
employee uses it.
View
or download PDF
(b)
Manhole
steps.
(1) The employer must ensure that each manhole step is capable of
supporting its maximum intended load.
(2)
The employer must ensure that each manhole step installed on or
after January 17, 2017:
(i)
Has a corrugated, knurled, dimpled, or other surface that
minimizes the possibility of an employee slipping;
(ii)
Is constructed of, or coated with, material that protects against
corrosion if the manhole step is located in an environment where
corrosion may occur;
(iii)
Has a minimum clear step width of 10 inches (25 cm);
(iv)
Is uniformly spaced at a vertical distance not more than 16 inches
(41 cm) apart, measured center to center between steps. The
spacing from the entry and exit surface to the first manhole step
may differ from the spacing between the other steps.
(v)
Has a minimum perpendicular distance between the centerline of the
manhole step to the nearest permanent object in back of the step
of at least 4.5 inches (11 cm); and
(vi)
Is designed, constructed, and maintained to prevent the employee's
foot from slipping or sliding off the end.
(3)
The employer must ensure that each manhole step is inspected at
the start of the work shift and maintained in accordance with
§1910.22.
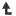 Back
to Top
Back
to Top
§1910.25 Stairways.
(a)
Application.
This section covers all stairways (including standard, spiral,
ship, and alternating tread-type stairs), except for stairs
serving floating roof tanks, stairs on scaffolds, stairs designed
into machines or equipment, and stairs on self-propelled motorized
equipment.
(b)
General
requirements.
The employer must ensure:
(1)
Handrails, stair rail systems, and guardrail systems are provided
in accordance with §1910.28;
(2)
Vertical clearance above any stair tread to any overhead
obstruction is at least 6 feet, 8 inches (203 cm), as measured
from the leading edge of the tread. Spiral stairs must meet the
vertical clearance requirements in paragraph (d)(3) of this
section.
(3)
Stairs have uniform riser heights and tread depths between
landings;
(4)
Stairway landings and platforms are at least the width of the
stair and at least 30 inches (76 cm) in depth, as measured in the
direction of travel;
(5)
When a door or a gate opens directly on a stairway, a platform is
provided, and the swing of the door or gate does not reduce the
platform's effective usable depth to:
(i)
Less than 20 inches (51 cm) for platforms installed before January
17, 2017; and
(ii)
Less than 22 inches (56 cm) for platforms installed on or after
January 17, 2017 (see Figure D-7 of this section);
(6)
Each stair can support at least five times the normal anticipated
live load, but never less than a concentrated load of 1,000 pounds
(454 kg) applied at any point;
(7)
Standard stairs are used to provide access from one
walking-working surface to another when operations necessitate
regular and routine travel between levels, including access to
operating platforms for equipment. Winding stairways may be used
on tanks and similar round structures when the diameter of the
tank or structure is at least 5 feet (1.5 m).
(8)
Spiral, ship, or alternating tread-type stairs are used only when
the employer can demonstrate that it is not feasible to provide
standard stairs.
(9)
When paragraph (b)(8) of this section allows the use of spiral,
ship, or alternating tread-type stairs, they are installed, used,
and maintained in accordance with manufacturer's instructions.
View
or download PDF
(c)
Standard
stairs.
In addition to paragraph (b) of this section, the employer must
ensure standard stairs:
(1)
Are installed at angles between 30 to 50 degrees from the
horizontal;
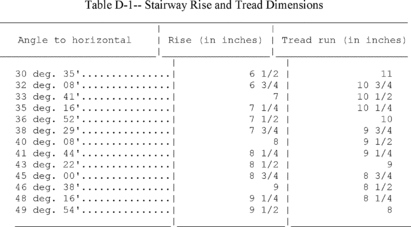
(2)
Have a maximum riser height of 9.5 inches (24 cm);
(3)
Have a minimum tread depth of 9.5 inches (24 cm); and
(4)
Have a minimum width of 22 inches (56 cm) between vertical
barriers (see Figure D-8 of this section).
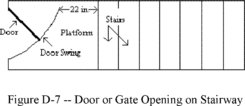
(5)
Exception
to paragraphs (c)(2) and (3) of this section.
The requirements of paragraphs (c)(2) and (3) do not apply to
standard stairs installed prior to January 17, 2017. OSHA will
deem those stairs in compliance if they meet the dimension
requirements specified in Table D-1 of this section or they use a
combination that achieves the angle requirements of paragraph
(c)(1) of this section.
View
or download PDF
View
or download PDF
(d)
Spiral
stairs.
In addition to paragraph (b) of this section, the employer must
ensure spiral stairs:
(1)
Have a minimum clear width of 26 inches (66 cm);
(2)
Have a maximum riser height of 9.5 inches (24 cm);
(3)
Have a minimum headroom above spiral stair treads of at least 6
feet, 6 inches (2 m), measured from the leading edge of the tread;
(4)
Have a minimum tread depth of 7.5 inches (19 cm), measured at a
point 12 inches (30 cm) from the narrower edge;
(5)
Have a uniform tread size;
(e)
Ship
stairs.
In addition to paragraph (b) of this section, the employer must
ensure ship stairs (see Figure D-9 of this section):
(1)
Are installed at a slope of 50 to 70 degrees from the horizontal;
(2)
Have open risers with a vertical rise between tread surfaces of
6.5 to 12 inches (17 to 30 cm);
(3)
Have minimum tread depth of 4 inches (10 cm); and
(4)
Have a minimum tread width of 18 inches (46 cm).
View
or download PDF
(f)
Alternating
tread-type stairs.
In addition to paragraph (b) of this section, the employer must
ensure alternating tread-type stairs:
(1)
Have a series of treads installed at a slope of 50 to 70 degrees
from the horizontal;
(2)
Have a distance between handrails of 17 to 24 inches (51 to 61
cm);
(3)
Have a minimum tread depth of 8.5 inches (22 cm); and
(4)
Have open risers if the tread depth is less than 9.5 inches (24
cm);
(5)
Have a minimum tread width of 7 inches (18 cm), measured at the
leading edge of the tread (i.e.,
nosing).
View
or download PDF
§1910.26 Dockboards.
The
employer must ensure that each dockboard used meets the
requirements of this section. The employer must ensure:
(a)
Dockboards are capable of supporting the maximum intended load in
accordance with §1910.22(b);
(b)(1)
Dockboards put into initial service on or after January 17, 2017
are designed, constructed, and maintained to prevent transfer
vehicles from running off the dockboard edge;
(2)
Exception
to paragraph (b)(1) of this section.
When the employer demonstrates there is no hazard of transfer
vehicles running off the dockboard edge, the employer may use
dockboards that do not have run-off protection.
(c)
Portable dockboards are secured by anchoring them in place or
using equipment or devices that prevent the dockboard from moving
out of a safe position. When the employer demonstrates that
securing the dockboard is not feasible, the employer must ensure
there is sufficient contact between the dockboard and the surface
to prevent the dockboard from moving out of a safe position;
(d)
Measures, such as wheel chocks or sand shoes, are used to prevent
the transport vehicle (e.g.
a truck, semi-trailer, trailer, or rail car) on which a dockboard
is placed, from moving while employees are on the dockboard; and
(e)
Portable dockboards are equipped with handholds or other means to
permit safe handling of dockboards.
§1910.27 Scaffolds
and rope descent systems.
(a)
Scaffolds.
Scaffolds used in general industry must meet the requirements in
29 CFR part 1926, subpart L (Scaffolds).
(b)
Rope
descent systems—(1)
Anchorages.
(i) Before any rope descent system is used, the building owner
must inform the employer, in writing that the building owner has
identified, tested, certified, and maintained each anchorage so it
is capable of supporting at least 5,000 pounds (268 kg), in any
direction, for each employee attached. The information must be
based on an annual inspection by a qualified person and
certification of each anchorage by a qualified person, as
necessary, and at least every 10 years.
(ii)
The employer must ensure that no employee uses any anchorage
before the employer has obtained written information from the
building owner that each anchorage meets the requirements of
paragraph (b)(1)(i) of this section. The employer must keep the
information for the duration of the job.
(iii)
The requirements in paragraphs (b)(1)(i) and (ii) of this section
must be implemented no later than November 20, 2017.
(2)
Use
of rope descent systems.
The employer must ensure:
(i)
No rope descent system is used for heights greater than 300 feet
(91 m) above grade unless the employer demonstrates that it is not
feasible to access such heights by any other means or that those
means pose a greater hazard than using a rope descent system;
(ii)
The rope descent system is used in accordance with instructions,
warnings, and design limitations set by the manufacturer or under
the direction of a qualified person;
(iii)
Each employee who uses the rope descent system is trained in
accordance with §1910.30;
(iv)
The rope descent system is inspected at the start of each
workshift that it is to be used. The employer must ensure damaged
or defective equipment is removed from service immediately and
replaced;
(v)
The rope descent system has proper rigging, including anchorages
and tiebacks, with particular emphasis on providing tiebacks when
counterweights, cornice hooks, or similar non-permanent anchorages
are used;
(vi)
Each employee uses a separate, independent personal fall arrest
system that meets the requirements of subpart I of this part;
(vii)
All components of each rope descent system, except seat boards,
are capable of sustaining a minimum rated load of 5,000 pounds
(22.2 kN). Seat boards must be capable of supporting a live load
of 300 pounds (136 kg);
(viii)
Prompt rescue of each employee is provided in the event of a fall;
(ix)
The ropes of each rope descent system are effectively padded or
otherwise protected, where they can contact edges of the building,
anchorage, obstructions, or other surfaces, to prevent them from
being cut or weakened;
(x)
Stabilization is provided at the specific work location when
descents are greater than 130 feet (39.6 m);
(xi)
No employee uses a rope descent system when hazardous weather
conditions, such as storms or gusty or excessive wind, are
present;
(xii)
Equipment, such as tools, squeegees, or buckets, is secured by a
tool lanyard or similar method to prevent it from falling; and
(xiii)
The ropes of each rope descent system are protected from exposure
to open flames, hot work, corrosive chemicals, and other
destructive conditions.
§1910.28 Duty
to have fall protection and falling object protection.
(a)
General.
(1) This section requires employers to provide protection for each
employee exposed to fall and falling object hazards. Unless stated
otherwise, the employer must ensure that all fall protection and
falling object protection required by this section meet the
criteria in §1910.29, except that personal fall protection
systems required by this section meet the criteria of §1910.140.
(2)
This section does not apply:
(i)
To portable ladders;
(ii)
When employers are inspecting, investigating, or assessing
workplace conditions or work to be performed prior to the start of
work or after all work has been completed. This exemption does not
apply when fall protection systems or equipment meeting the
requirements of §1910.29 have been installed and are
available for workers to use for pre-work and post-work
inspections, investigations, or assessments;
(iii)
To fall hazards presented by the exposed perimeters of
entertainment stages and the exposed perimeters of rail-station
platforms;
(iv)
To powered platforms covered by §1910.66(j);
(v)
To aerial lifts covered by §1910.67(c)(2)(v);
(vi)
To telecommunications work covered by §1910.268(n)(7) and
(8); and
(vii)
To electric power generation, transmission, and distribution work
covered by §1910.269(g)(2)(i).
(b)
Protection
from fall hazards—(1)
Unprotected
sides and edges.
(i) Except as provided elsewhere in this section, the employer
must ensure that each employee on a walking-working surface with
an unprotected side or edge that is 4 feet (1.2 m) or more above a
lower level is protected from falling by one or more of the
following:
(A)
Guardrail systems;
(B)
Safety net systems; or
(C)
Personal fall protection systems, such as personal fall arrest,
travel restraint, or positioning systems.
(ii)
When the employer can demonstrate that it is not feasible or
creates a greater hazard to use guardrail, safety net, or personal
fall protection systems on residential roofs, the employer must
develop and implement a fall protection plan that meets the
requirements of 29 CFR 1926.502(k) and training that meets the
requirements of 29 CFR 1926.503(a) and (c).
Note
to paragraph (b)(1)(ii)
of this section:
There is a presumption that it is feasible and will not create a
greater hazard to use at least one of the above-listed fall
protection systems specified in paragraph (b)(1)(i) of this
section. Accordingly, the employer has the burden of establishing
that it is not feasible or creates a greater hazard to provide the
fall protection systems specified in paragraph (b)(1)(i) and that
it is necessary to implement a fall protection plan that complies
with §1926.502(k) in the particular work operation, in lieu
of implementing any of those systems.
(iii)
When the employer can demonstrate that the use of fall protection
systems is not feasible on the working side of a platform used at
a loading rack, loading dock, or teeming platform, the work may be
done without a fall protection system, provided:
(A)
The work operation for which fall protection is infeasible is in
process;
(B)
Access to the platform is limited to authorized employees; and,
(C)
The authorized employees are trained in accordance with §1910.30.
(2)
Hoist
areas.
The employer must ensure:
(i)
Each employee in a hoist area is protected from falling 4 feet
(1.2 m) or more to a lower level by:
(A)
A guardrail system;
(B)
A personal fall arrest system; or
(C)
A travel restraint system.
(ii)
When any portion of a guardrail system, gate, or chains is
removed, and an employee must lean through or over the edge of the
access opening to facilitate hoisting, the employee is protected
from falling by a personal fall arrest system.
(iii)
If grab handles are installed at hoist areas, they meet the
requirements of §1910.29(l).
(3)
Holes.
The employer must ensure:
(i)
Each employee is protected from falling through any hole
(including skylights) that is 4 feet (1.2 m) or more above a lower
level by one or more of the following:
(A)
Covers;
(B)
Guardrail systems;
(C)
Travel restraint systems; or
(D)
Personal fall arrest systems.
(ii)
Each employee is protected from tripping into or stepping into or
through any hole that is less than 4 feet (1.2 m) above a lower
level by covers or guardrail systems.
(iii)
Each employee is protected from falling into a stairway floor hole
by a fixed guardrail system on all exposed sides, except at the
stairway entrance. However, for any stairway used less than once
per day where traffic across the stairway floor hole prevents the
use of a fixed guardrail system (e.g.,
holes located in aisle spaces), the employer may protect employees
from falling into the hole by using a hinged floor hole cover that
meets the criteria in §1910.29 and a removable guardrail
system on all exposed sides, except at the entrance to the
stairway.
(iv)
Each employee is protected from falling into a ladderway floor
hole or ladderway platform hole by a guardrail system and
toeboards erected on all exposed sides, except at the entrance to
the hole, where a self-closing gate or an offset must be used.
(v)
Each employee is protected from falling through a hatchway and
chute-floor hole by:
(A)
A hinged floor-hole cover that meets the criteria in §1910.29
and a fixed guardrail system that leaves only one exposed side.
When the hole is not in use, the employer must ensure the cover is
closed or a removable guardrail system is provided on the exposed
sides;
(B)
A removable guardrail system and toeboards on not more than two
sides of the hole and a fixed guardrail system on all other
exposed sides. The employer must ensure the removable guardrail
system is kept in place when the hole is not in use; or
(C)
A guardrail system or a travel restraint system when a work
operation necessitates passing material through a hatchway or
chute floor hole.
(4)
Dockboards.
(i) The employer must ensure that each employee on a dockboard is
protected from falling 4 feet (1.2 m) or more to a lower level by
a guardrail system or handrails.
(ii)
A guardrail system or handrails are not required when:
(A)
Dockboards are being used solely for materials-handling operations
using motorized equipment;
(B)
Employees engaged in these operations are not exposed to fall
hazards greater than 10 feet (3 m); and
(C)
Those employees have been trained in accordance with §1910.30.
(5)
Runways
and similar walkways.
(i) The employer must ensure each employee on a runway or similar
walkway is protected from falling 4 feet (1.2 m) or more to a
lower level by a guardrail system.
(ii)
When the employer can demonstrate that it is not feasible to have
guardrails on both sides of a runway used exclusively for a
special purpose, the employer may omit the guardrail on one side
of the runway, provided the employer ensures:
(A)
The runway is at least 18 inches (46 cm) wide; and
(B)
Each employee is provided with and uses a personal fall arrest
system or travel restraint system.
(6)
Dangerous
equipment.
The employer must ensure:
(i)
Each employee less than 4 feet (1.2 m) above dangerous equipment
is protected from falling into or onto the dangerous equipment by
a guardrail system or a travel restraint system, unless the
equipment is covered or guarded to eliminate the hazard.
(ii)
Each employee 4 feet (1.2 m) or more above dangerous equipment
must be protected from falling by:
(A)
Guardrail systems;
(B)
Safety net systems;
(C)
Travel restraint systems; or
(D)
Personal fall arrest systems.
(7)
Openings.
The employer must ensure that each employee on a walking-working
surface near an opening, including one with a chute attached,
where the inside bottom edge of the opening is less than 39 inches
(99 cm) above that walking-working surface and the outside bottom
edge of the opening is 4 feet (1.2 m) or more above a lower level
is protected from falling by the use of:
(i)
Guardrail systems;
(ii)
Safety net systems;
(iii)
Travel restraint systems; or,
(iv)
Personal fall arrest systems.
(8)
Repair
pits, service pits, and assembly pits less than 10 feet in depth.
The use of a fall protection system is not required for a repair
pit, service pit, or assembly pit that is less than 10 feet (3 m)
deep, provided the employer:
(i)
Limits access within 6 feet (1.8 m) of the edge of the pit to
authorized employees trained in accordance with §1910.30;
(ii)
Applies floor markings at least 6 feet (1.8 m) from the edge of
the pit in colors that contrast with the surrounding area; or
places a warning line at least 6 feet (1.8 m) from the edge of the
pit as well as stanchions that are capable of resisting, without
tipping over, a force of at least 16 pounds (71 N) applied
horizontally against the stanchion at a height of 30 inches (76
cm); or places a combination of floor markings and warning lines
at least 6 feet (1.8 m) from the edge of the pit. When two or more
pits in a common area are not more than 15 feet (4.5m) apart, the
employer may comply by placing contrasting floor markings at least
6 feet (1.8 m) from the pit edge around the entire area of the
pits; and
(iii)
Posts readily visible caution signs that meet the requirements of
§1910.145 and state “Caution—Open Pit.”
(9)
Fixed
ladders (that extend more than 24 feet (7.3 m) above a lower
level).
(i) For fixed ladders that extend more than 24 feet (7.3 m) above
a lower level, the employer must ensure:
(A)
Existing
fixed ladders.
Each fixed ladder installed before November 19, 2018 is equipped
with a personal fall arrest system, ladder safety system, cage, or
well;
(B)
New
fixed ladders.
Each fixed ladder installed on and after November 19, 2018, is
equipped with a personal fall arrest system or a ladder safety
system;
(C)
Replacement.
When a fixed ladder, cage, or well, or any portion of a section
thereof, is replaced, a personal fall arrest system or ladder
safety system is installed in at least that section of the fixed
ladder, cage, or well where the replacement is located; and
(D)
Final
deadline.
On and after November 18, 2036, all fixed ladders are equipped
with a personal fall arrest system or a ladder safety system.
(ii)
When a one-section fixed ladder is equipped with a personal fall
protection or a ladder safety system or a fixed ladder is equipped
with a personal fall arrest or ladder safety system on more than
one section, the employer must ensure:
(A)
The personal fall arrest system or ladder safety system provides
protection throughout the entire vertical distance of the ladder,
including all ladder sections; and
(B)
The ladder has rest platforms provided at maximum intervals of 150
feet (45.7 m).
(iii)
The employer must ensure ladder sections having a cage or well:
(A)
Are offset from adjacent sections; and
(B)
Have landing platforms provided at maximum intervals of 50 feet
(15.2 m).
(iv)
The employer may use a cage or well in combination with a personal
fall arrest system or ladder safety system provided that the cage
or well does not interfere with the operation of the system.
(10)
Outdoor
advertising (billboards).
(i) The requirements in paragraph (b)(9) of this section, and
other requirements in subparts D and I of this part, apply to
fixed ladders used in outdoor advertising activities.
(ii)
When an employee engaged in outdoor advertising climbs a fixed
ladder before November 19, 2018 that is not equipped with a cage,
well, personal fall arrest system, or a ladder safety system the
employer must ensure the employee:
(A)
Receives training and demonstrates the physical capability to
perform the necessary climbs in accordance with §1910.29(h);
(B)
Wears a body harness equipped with an 18-inch (46 cm) rest
lanyard;
(C)
Keeps both hands free of tools or material when climbing on the
ladder; and
(D)
Is protected by a fall protection system upon reaching the work
position.
(11)
Stairways.
The employer must ensure:
(i)
Each employee exposed to an unprotected side or edge of a stairway
landing that is 4 feet (1.2 m) or more above a lower level is
protected by a guardrail or stair rail system;
(ii)
Each flight of stairs having at least 3 treads and at least 4
risers is equipped with stair rail systems and handrails as
follows:
View
or download PDF
(iii)
Each ship stairs and alternating tread type stairs is equipped
with handrails on both sides.
(12)
Scaffolds
and rope descent systems.
The employer must ensure:
(i)
Each employee on a scaffold is protected from falling in
accordance 29 CFR part 1926, subpart L; and
(ii)
Each employee using a rope descent system 4 feet (1.2 m) or more
above a lower level is protected from falling by a personal fall
arrest system.
(13)
Work
on low-slope roofs.
(i) When work is performed less than 6 feet (1.6 m) from the roof
edge, the employer must ensure each employee is protected from
falling by a guardrail system, safety net system, travel restraint
system, or personal fall arrest system.
(ii)
When work is performed at least 6 feet (1.6 m) but less than 15
feet (4.6 m) from the roof edge, the employer must ensure each
employee is protected from falling by using a guardrail system,
safety net system, travel restraint system, or personal fall
arrest system. The employer may use a designated area when
performing work that is both infrequent and temporary.
(iii)
When work is performed 15 feet (4.6 m) or more from the roof edge,
the employer must:
(A)
Protect each employee from falling by a guardrail system, safety
net system, travel restraint system, or personal fall arrest
system or a designated area. The employer is not required to
provide any fall protection, provided the work is both infrequent
and temporary; and
(B)
Implement and enforce a work rule prohibiting employees from going
within 15 feet (4.6 m) of the roof edge without using fall
protection in accordance with paragraphs (b)(13)(i) and (ii) of
this section.
(14)
Slaughtering
facility platforms.
(i) The employer must protect each employee on the unprotected
working side of a slaughtering facility platform that is 4 feet
(1.2 m) or more above a lower level from falling by using:
(A)
Guardrail systems; or
(B)
Travel restraint systems.
(ii)
When the employer can demonstrate the use of a guardrail or travel
restraint system is not feasible, the work may be done without
those systems provided:
(A)
The work operation for which fall protection is infeasible is in
process;
(B)
Access to the platform is limited to authorized employees; and
(C)
The authorized employees are trained in accordance with §1910.30.
(15)
Walking-working
surfaces not otherwise addressed.
Except as provided elsewhere in this section or by other subparts
of this part, the employer must ensure each employee on a
walking-working surface 4 feet (1.2 m) or more above a lower level
is protected from falling by:
(i)
Guardrail systems;
(ii)
Safety net systems; or
(iii)
Personal fall protection systems, such as personal fall arrest,
travel restraint, or positioning systems.
(c)
Protection
from falling objects.
When an employee is exposed to falling objects, the employer must
ensure that each employee wears head protection that meets the
requirements of subpart I of this part. In addition, the employer
must protect employees from falling objects by implementing one or
more of the following:
(1)
Erecting toeboards, screens, or guardrail systems to prevent
objects from falling to a lower level;
(2)
Erecting canopy structures and keeping potential falling objects
far enough from an edge, hole, or opening to prevent them from
falling to a lower level; or
(3)
Barricading the area into which objects could fall, prohibiting
employees from entering the barricaded area, and keeping objects
far enough from an edge or opening to prevent them from falling to
a lower level.
§1910.29 Fall
protection systems and falling object protection—criteria
and practices.
(a)
General
requirements.
The employer must:
(1)
Ensure each fall protection system and falling object protection,
other than personal fall protection systems, that this part
requires meets the requirements in this section. The employer must
ensure each personal fall protection system meets the requirements
in subpart I of this part; and
(2)
Provide and install all fall protection systems and falling object
protection this subpart requires, and comply with the other
requirements in this subpart before any employee begins work that
necessitates fall or falling object protection.
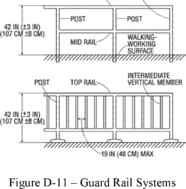
(b)
Guardrail
systems.
The employer must ensure guardrail systems meet the following
requirements:
(1)
The top edge height of top rails, or equivalent guardrail system
members, are 42 inches (107 cm), plus or minus 3 inches (8 cm),
above the walking-working surface. The top edge height may exceed
45 inches (114 cm), provided the guardrail system meets all other
criteria of paragraph (b) of this section (see Figure D-11 of this
section).
(2)
Midrails, screens, mesh, intermediate vertical members, solid
panels, or equivalent intermediate members are installed between
the walking-working surface and the top edge of the guardrail
system as follows when there is not a wall or parapet that is at
least 21 inches (53 cm) high:
(i)
Midrails are installed at a height midway between the top edge of
the guardrail system and the walking-working surface;
(ii)
Screens and mesh extend from the walking-working surface to the
top rail and along the entire opening between top rail supports;
(iii)
Intermediate vertical members (such as balusters) are installed no
more than 19 inches (48 cm) apart; and
(iv)
Other equivalent intermediate members (such as additional midrails
and architectural panels) are installed so that the openings are
not more than 19 inches (48 cm) wide.
(3)
Guardrail systems are capable of withstanding, without failure, a
force of at least 200 pounds (890 N) applied in a downward or
outward direction within 2 inches (5 cm) of the top edge, at any
point along the top rail.
(4)
When the 200-pound (890-N) test load is applied in a downward
direction, the top rail of the guardrail system must not deflect
to a height of less than 39 inches (99 cm) above the
walking-working surface.
(5)
Midrails, screens, mesh, intermediate vertical members, solid
panels, and other equivalent intermediate members are capable of
withstanding, without failure, a force of at least 150 pounds (667
N) applied in any downward or outward direction at any point along
the intermediate member.
(6)
Guardrail systems are smooth-surfaced to protect employees from
injury, such as punctures or lacerations, and to prevent catching
or snagging of clothing.
(7)
The ends of top rails and midrails do not overhang the terminal
posts, except where the overhang does not pose a projection hazard
for employees.
(8)
Steel banding and plastic banding are not used for top rails or
midrails.
(9)
Top rails and midrails are at least 0.25-inches (0.6 cm) in
diameter or in thickness.
(10)
When guardrail systems are used at hoist areas, a removable
guardrail section, consisting of a top rail and midrail, are
placed across the access opening between guardrail sections when
employees are not performing hoisting operations. The employer may
use chains or gates instead of a removable guardrail section at
hoist areas if the employer demonstrates the chains or gates
provide a level of safety equivalent to guardrails.
(11)
When guardrail systems are used around holes, they are installed
on all unprotected sides or edges of the hole.
(12)
For guardrail systems used around holes through which materials
may be passed:
(i)
When materials are being passed through the hole, not more than
two sides of the guardrail system are removed; and
(ii)
When materials are not being passed through the hole, the hole
must be guarded by a guardrail system along all unprotected sides
or edges or closed over with a cover.
(13)
When guardrail systems are used around holes that serve as points
of access (such as ladderways), the guardrail system opening:
(i)
Has a self-closing gate that slides or swings away from the hole,
and is equipped with a top rail and midrail or equivalent
intermediate member that meets the requirements in paragraph (b)
of this section; or
(ii)
Is offset to prevent an employee from walking or falling into the
hole;
(14)
Guardrail systems on ramps and runways are installed along each
unprotected side or edge.
(15)
Manila or synthetic rope used for top rails or midrails are
inspected as necessary to ensure that the rope continues to meet
the strength requirements in paragraphs (b)(3) and (5) of this
section.
Note
to paragraph (b)
of this section:
The criteria and practices requirements for guardrail systems on
scaffolds are contained in 29 CFR part 1926, subpart L.
View
or download PDF
(c)
Safety
net systems.
The employer must ensure each safety net system meets the
requirements in 29 CFR part 1926, subpart M.
(d)
Designated
areas.
(1) When the employer uses a designated area, the employer must
ensure:
(i)
Employees remain within the designated area while work operations
are underway; and
(ii)
The perimeter of the designated area is delineated with a warning
line consisting of a rope, wire, tape, or chain that meets the
requirements of paragraphs (d)(2) and (3) of this section.
(2)
The employer must ensure each warning line:
(i)
Has a minimum breaking strength of 200 pounds (0.89 kN);
(ii)
Is installed so its lowest point, including sag, is not less than
34 inches (86 cm) and not more than 39 inches (99 cm) above the
walking-working surface;
(iii)
Is supported in such a manner that pulling on one section of the
line will not result in slack being taken up in adjacent sections
causing the line to fall below the limits specified in paragraph
(d)(2)(ii) of this section;
(iv)
Is clearly visible from a distance of 25 feet (7.6 m) away, and
anywhere within the designated area;
(v)
Is erected as close to the work area as the task permits; and
(vi)
Is erected not less than 6 feet (1.8 m) from the roof edge for
work that is both temporary and infrequent, or not less than 15
feet (4.6 m) for other work.
(3)
When mobile mechanical equipment is used to perform work that is
both temporary and infrequent in a designated area, the employer
must ensure the warning line is erected not less than 6 feet (1.8
m) from the unprotected side or edge that is parallel to the
direction in which the mechanical equipment is operated, and not
less than 10 feet (3 m) from the unprotected side or edge that is
perpendicular to the direction in which the mechanical equipment
is operated.
(e)
Covers.
The employer must ensure each cover for a hole in a
walking-working surface:
(1)
Is capable of supporting without failure, at least twice the
maximum intended load that may be imposed on the cover at any one
time; and
(2)
Is secured to prevent accidental displacement.
(f)
Handrails
and stair rail systems.
The employer must ensure:
(1)
Height
criteria.
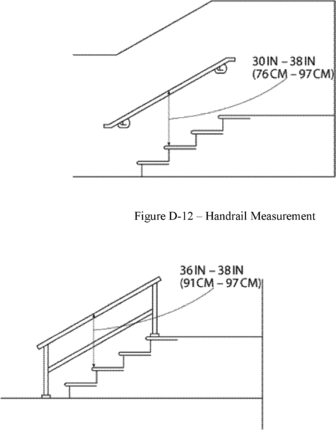
(i) Handrails are not less than 30 inches (76 cm) and not more
than 38 inches (97 cm), as measured from the leading edge of the
stair tread to the top surface of the handrail (see Figure D-12 of
this section).
(ii)
The height of stair rail systems meets the following:
(A)
The height of stair rail systems installed before January 17, 2017
is not less than 30 inches (76 cm) from the leading edge of the
stair tread to the top surface of the top rail; and
(B)
The height of stair rail systems installed on or after January 17,
2017 is not less than 42 inches (107 cm) from the leading edge of
the stair tread to the top surface of the top rail.
(iii)
The top rail of a stair rail system may serve as a handrail only
when:
(A)
The height of the stair rail system is not less than 36 inches (91
cm) and not more than 38 inches (97 cm) as measured at the leading
edge of the stair tread to the top surface of the top rail (see
Figure D-13 of this section); and
(B)
The top rail of the stair rail system meets the other handrail
requirements in paragraph (f) of this section.
(2)
Finger
clearance.
The minimum clearance between handrails and any other object is
2.25 inches (5.7 cm).
(3)
Surfaces.
Handrails and stair rail systems are smooth-surfaced to protect
employees from injury, such as punctures or lacerations, and to
prevent catching or snagging of clothing.
(4)
Openings
in stair rails.
No opening in a stair rail system exceeds 19 inches (48 cm) at its
least dimension.
(5)
Handhold.
Handrails have the shape and dimension necessary so that employees
can grasp the handrail firmly.
(6)
Projection
hazards.
The ends of handrails and stair rail systems do not present any
projection hazards.
(7)
Strength
criteria.
Handrails and the top rails of stair rail systems are capable of
withstanding, without failure, a force of at least 200 pounds (890
N) applied in any downward or outward direction within 2 inches (5
cm) of any point along the top edge of the rail.
View
or download PDF
|
|
|
Figure
D-13 - Combination Handrail and Stair Rail
|
(g)
Cages,
wells, and platforms used with fixed ladders.
The employer must ensure:
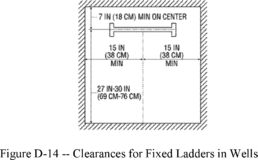
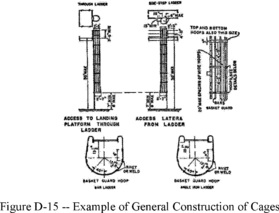
(1)
Cages and wells installed on fixed ladders are designed,
constructed, and maintained to permit easy access to, and egress
from, the ladder that they enclose (see Figures D-14 and D-15 of
this section);
(2)
Cages and wells are continuous throughout the length of the fixed
ladder, except for access, egress, and other transfer points;
(3)
Cages and wells are designed, constructed, and maintained to
contain employees in the event of a fall, and to direct them to a
lower landing; and
(4)
Platforms used with fixed ladders provide a horizontal surface of
at least 24 inches by 30 inches (61 cm by 76 cm).
Note
to paragraph (g):
Section 1910.28 establishes the requirements that employers must
follow on the use of cages and wells as a means of fall
protection.
View
or download PDF
View
or download PDF
(h)
Outdoor
advertising.
This paragraph (h) applies only to employers engaged in outdoor
advertising operations (see §1910.28(b)(10)). Employers must
ensure that each employee who climbs a fixed ladder without fall
protection:
(1)
Is physically capable, as demonstrated through observations of
actual climbing activities or by a physical examination, to
perform the duties that may be assigned, including climbing fixed
ladders without fall protection;
(2)
Has successfully completed a training or apprenticeship program
that includes hands-on training on the safe climbing of ladders
and is retrained as necessary to maintain the necessary skills;
(3)
Has the skill to climb ladders safely, as demonstrated through
formal classroom training or on-the-job training, and performance
observation; and
(4)
Performs climbing duties as a part of routine work activity.
(i)
Ladder
safety systems.
The employer must ensure:
(1)
Each ladder safety system allows the employee to climb up and down
using both hands and does not require that the employee
continuously hold, push, or pull any part of the system while
climbing;
(2)
The connection between the carrier or lifeline and the point of
attachment to the body harness or belt does not exceed 9 inches
(23 cm);
(3)
Mountings for rigid carriers are attached at each end of the
carrier, with intermediate mountings spaced, as necessary, along
the entire length of the carrier so the system has the strength to
stop employee falls;
(4)
Mountings for flexible carriers are attached at each end of the
carrier and cable guides for flexible carriers are installed at
least 25 feet (7.6 m) apart but not more than 40 feet (12.2 m)
apart along the entire length of the carrier;
(5)
The design and installation of mountings and cable guides does not
reduce the design strength of the ladder; and
(6)
Ladder safety systems and their support systems are capable of
withstanding, without failure, a drop test consisting of an
18-inch (41-cm) drop of a 500-pound (227-kg) weight.
(j)
Personal
fall protection systems.
Body belts, harnesses, and other components used in personal fall
arrest systems, work positioning systems, and travel restraint
systems must meet the requirements of §1910.140.
(k)
Protection
from falling objects.
(1) The employers must ensure toeboards used for falling object
protection:
(i)
Are erected along the exposed edge of the overhead walking-working
surface for a length that is sufficient to protect employees
below.
(ii)
Have a minimum vertical height of 3.5 inches (9 cm) as measured
from the top edge of the toeboard to the level of the
walking-working surface.
(iii)
Do not have more than a 0.25-inch (0.5-cm) clearance or opening
above the walking-working surface.
(iv)
Are solid or do not have any opening that exceeds 1 inch (3 cm) at
its greatest dimension.
(v)
Have a minimum height of 2.5 inches (6 cm) when used around
vehicle repair, service, or assembly pits. Toeboards may be
omitted around vehicle repair, service, or assembly pits when the
employer can demonstrate that a toeboard would prevent access to a
vehicle that is over the pit.
(vi)
Are capable of withstanding, without failure, a force of at least
50 pounds (222 N) applied in any downward or outward direction at
any point along the toeboard.
(2)
The employer must ensure:
(i)
Where tools, equipment, or materials are piled higher than the top
of the toeboard, paneling or screening is installed from the
toeboard to the midrail of the guardrail system and for a length
that is sufficient to protect employees below. If the items are
piled higher than the midrail, the employer also must install
paneling or screening to the top rail and for a length that is
sufficient to protect employees below; and
(ii)
All openings in guardrail systems are small enough to prevent
objects from falling through the opening.
(3)
The employer must ensure canopies used for falling object
protection are strong enough to prevent collapse and to prevent
penetration by falling objects.
(l)
Grab
handles.
The employer must ensure each grab handle:
(1)
Is not less than 12 inches (30 cm) long;
(2)
Is mounted to provide at least 3 inches (8 cm) of clearance from
the framing or opening; and
(3)
Is capable of withstanding a maximum horizontal pull-out force
equal to two times the maximum intended load or 200 pounds (890
N), whichever is greater.
§1910.30 Training
requirements.
(a)
Fall
hazards.
(1) Before any employee is exposed to a fall hazard, the employer
must provide training for each employee who uses personal fall
protection systems or who is required to be trained as specified
elsewhere in this subpart. Employers must ensure employees are
trained in the requirements of this paragraph on or before May 17,
2017.
(2)
The employer must ensure that each employee is trained by a
qualified person.
(3)
The employer must train each employee in at least the following
topics:
(i)
The nature of the fall hazards in the work area and how to
recognize them;
(ii)
The procedures to be followed to minimize those hazards;
(iii)
The correct procedures for installing, inspecting, operating,
maintaining, and disassembling the personal fall protection
systems that the employee uses; and
(iv)
The correct use of personal fall protection systems and equipment
specified in paragraph (a)(1) of this section, including, but not
limited to, proper hook-up, anchoring, and tie-off techniques, and
methods of equipment inspection and storage, as specified by the
manufacturer.
(b)
Equipment
hazards.
(1) The employer must train each employee on or before May 17,
2017 in the proper care, inspection, storage, and use of equipment
covered by this subpart before an employee uses the equipment.
(2)
The employer must train each employee who uses a dockboard to
properly place and secure it to prevent unintentional movement.
(3)
The employer must train each employee who uses a rope descent
system in proper rigging and use of the equipment in accordance
with §1910.27.
(4)
The employer must train each employee who uses a designated area
in the proper set-up and use of the area.
(c)
Retraining.
The employer must retrain an employee when the employer has reason
to believe the employee does not have the understanding and skill
required by paragraphs (a) and (b) of this section. Situations
requiring retraining include, but are not limited to, the
following:
(1)
When changes in the workplace render previous training obsolete or
inadequate;
(2)
When changes in the types of fall protection systems or equipment
to be used render previous training obsolete or inadequate; or
(3)
When inadequacies in an affected employee's knowledge or use of
fall protection systems or equipment indicate that the employee no
longer has the requisite understanding or skill necessary to use
equipment or perform the job safely.
(d)
Training
must be understandable.
The employer must provide information and training to each
employee in a manner that the employee understands.
|













